Tibial intraosseous access in the pediatric population
“Aim of this study was to analyze anatomic dimensions of the proximal tibia in the pediatric population with respect to intraosseous needle placement and needle tip position” Capobianco et al (2020).
Prehospital use of peripheral intravenous catheters and intraosseous devices
“Peripheral intravenous catheters and intraosseous devices have been widely used in the prehospital setting for a considerable period” Mason et al (2020).
Analytical equivalence of intraosseous and peripheral blood samples
“While IO devices are effective for infusion of blood, fluids, and medications, there is limited data on the analytical equivalence of specimens taken out of IO devices and peripheral venous blood” Song et al (2020).
When should intraosseous access be considered a first-line option?
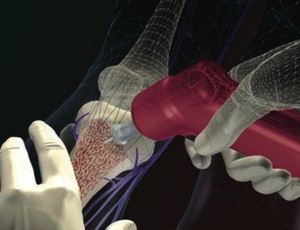
“In cases in which there is an urgent need for medications and fluid resuscitation, whether in infants, children, or adults, and immediate intravenous access is not easily obtainable, intraosseous access should be considered as a first-line option” DeBoer et al (2020).
Iatrogenic humeral neck fracture after intraosseous vascular access
“It is important for radiologists to recognize the findings related to intraosseous access as well as this complication with its characteristic locations and morphology” Hopp et al (2020).
Pediatric tibial intraosseous Epinephrine administration

“We compared the efficacy of tibial intraosseous (TIO) administration of epinephrine in a pediatric normovolemic versus hypovolemic cardiac arrest model” Yauger et al (2020).
Intraosseous access result in secondary septic shock – Full Text
“Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) created more confusion by showing septic arthritis with proximal humeral osteomyelitis and gas formation. MRI suggested that it might be the sequelae of an intraosseous line insertion” Khan et al (2020).
Intraosseous access in pediatric emergency care

“Intraosseous Access (IO) has obtained an increasingly valued place in emergency medical care cases when peripheral access venous access in not possible” Kikodze et al (2020).
Intravenous versus intraosseous administration of drugs during cardiac arrest
“To perform a systematic review of the literature on intravenous (IV) vs. intraosseous (IO) administration of drugs during cardiac arrest in order to inform an update of international guidelines” Granfeldt et al (2020).
Intraosseous versus peripheral IV access during out-of-hospital cardiac arrest

“To compare intraosseous access with peripheral venous access on adults out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) patients’ clinical outcomes” Baert et al (2020).
Prehospital life-saving interventions performed on pediatric patients in a combat zone

“We aimed to describe and evaluate prehospital life-saving interventions performed in a pediatric population in the Afghanistan theater of operations” Reeves et al (2020).
Effects of humeral intraosseous epinephrine in a pediatric hypovolemic cardiac arrest porcine model

“Aims of the study were to determine the effects of humerus intraosseous (HIO) versus intravenous (IV) administration of epinephrine in a hypovolemic, pediatric pig model” Neill et al (2020).
Overview of intraosseous vascular access

“Intraosseous (IO) vascular access refers to the placement of a specialized hollow bore needle through the cortex of a bone, into the medullary space for infusion of medical therapy and laboratory tests” Dornhofer and Kellar (2020).
Blood transfusion via intravenous and intraosseous access

“There was therefore the need for feasibility testing of a model for contrasting the efficacy of blood infusion devices via intravenous (IV) and IO access” Bianchi et al (2020).
Intraosseous adrenaline for adult out-of-hospital cardiac arrest

“Intraosseous adrenaline for adult out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: Faster access with worse outcomes” Morgan et al (2020).
Intraosseous access in the resuscitation of trauma patients

“The objective of this review was to examine the evidence for intraosseous catheters in trauma resuscitation, and to highlight areas for future research” Tyler et al (2020).
Whole blood infusion via the IO route in traumatic hemorrhagic shock

“This is the first report of whole blood infusion via the IO route in traumatic hemorrhagic shock in the prehospital setting” Allon et al (2020).
IV versus intraosseous adrenaline administration in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest

“The 2018 Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS) algorithm gives the option of either intravenous (IV) or intraosseous (IO) routes for adrenaline administration during cardiac arrest” Zhang et al (2020).
Intraosseous versus intravenous drug administration in patients with out-of-hospital cardiac arrest

“To compare the effectiveness of the intravenous (IV) and intraosseous (IO) routes for drug administration in adults with a cardiac arrest enrolled in the Pre-Hospital Assessment of the Role of Adrenaline” Nolan et al (2020).
Intraosseous access sites in rabbits
“The study goals were to determine if intraosseous (IO) catheters can be placed with greater success into the humerus, femur, or tibia of cadaver rabbits, and to evaluate the accuracy of perceived success (PS) and objective clinical success (OCS) criteria against true intramedullary catheterization confirmed by fluoroscopy” Kennedy et al (2020).
Intraosseous access in adults in cardiac arrest

“To evaluate the efficacy of intraosseous access versus venous access in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in terms of return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC) and survival to hospital discharge with or without favorable neurologic status” Morales-Cané et al (2020).
TXA administration via IO and IM routes during hemorrhagic shock

TXA administration via IO and IM routes during hemorrhagic shock achieves serum concentrations necessary for inhibition of fibrinolysis and may be practical alternatives when IV access is not available” DeSoucy et al (2020).
Survival after intravenous versus intraosseous Amiodarone

Survival to hospital admission also increased significantly when drugs were given IV but not IO, and favored improved neurological outcome at discharge” Daya et al (2020). Abstract: Background: Antiarrhythmic drugs have not proven to significantly improve overall survival after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) from shock-refractory ventricular fibrillation/pulseless ventricular tachycardia (VF/VT). How this might be influenced […]
Propionibacterium acnes osteomyelitis after intraosseous cannulation
We report here an extremely rare incident of P. acnes tibial osteomyelitis at the IO access site” Cole et al (2019). Abstract: Propionibacterium acnes osteomyelitis secondary to intraosseous (IO) cannulation is not well documented in literature. We report here an extremely rare incident of P. acnes tibial osteomyelitis at the IO access site, in a […]
Defined strategy for intraosseous devices in small children

Our study shows that the current procedure for establishing an intraosseous access in infants and children should also be critically reviewed” Maxien and Wirth (2019). Extract: We are grateful for the important remarks by Dr Bouchut and colleagues. The letter highlights a highly relevant and interesting aspect of the topic. The saying “children are not […]
Are intraosseous infusion needles long enough for children?

The EZ-IO intraosseous (IO) needle is available in 2 needle sizes for children based on the patient weight. To date, there is no published evidence validating the use of weight-based scaling in children. We hypothesized that pretibial subcutaneous tissue thickness (PSTT) does not correspond with patient weight but rather with age and body mass index […]
Intraosseous access devices in small children

Perhaps a more suitable question would be: which strategy adopt based on the type of IO device used, the age of the child and the location of the IO site?” Peguet et al (2019). Extract: We read with great interest the recently published study by Maxien et al. on the rate of malposition of intraosseous […]
Intraosseous catheterization during pediatric resuscitation

Our objective is to identify factors associated with the attempt and timing of IO catheterization in a pediatric emergency department (ED) resuscitation setting” Lee et al (2019). Abstract: STUDY OBJECTIVE: Factors associated with intraosseous (IO) catheterization are not well described. Our objective is to identify factors associated with the attempt and timing of IO catheterization […]
Intraosseous administration of 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate
We describe a case of a 69-year-old female receiving oral apixaban that was successfully administered 4F-PCC using intraosseous access prior to emergent surgery to obtain haemostasis intraoperatively” Ratliff et al (2019). Abstract: WHAT IS KNOWN AND OBJECTIVE: The 4-factor prothrombin complex concentrate (4F-PCC) may be used to emergently achieve haemostasis in patients on anticoagulation prior […]
Tibial intraosseous insertion in pediatric emergency care

In infants 6 months of age or younger, tibial IO needle insertion had a 53% failure rate (non-medullary placement)” Harcke et al (2019). Abstract: OBJECTIVE: The proximal tibia is a recommended and commonly used site for pediatric emergency intraosseous vascular access (IO). During forensic whole body postmortem computed tomography (PMCT), we evaluated accuracy of emergency […]

