Candida auris central line infection

“We report the first isolate of C. auris in Cali, Colombia, from a central venous catheter in a 37-year-old patient with rheumatoid arthritis and endocarditis who did not have symptoms of sepsis” Castro et al (2019).
PICC management in elderly patients

“These results suggest that PICC is useful and does not cause serious adverse effects, even in elderly patients who require central parenteral nutrition management” Ishiyama and Sudo (2020).
UEDVT incidence in pediatric patients after cardiac transplant

“We aimed to study the incidence of CATs and the impact of a risk-stratified anticoagulation protocol in reducing their development” Kirk et al (2020).
Vascular access and IV fluid administration during airborne evacuation

“The objective of this study was to evaluate the emergency care provided by the Israeli Military Airborne Combat Evacuation Unit (MACEU) during helicopter winching operations” Guinzburg et al (2020).
Pediatric central venous catheter complication risk factors

“The purpose of the study was to identify and to evaluate complications risk factors related to central venous catheterization” Rehn et al (2020).
What is the stability of different vancomycin solutions – Full Text
“The aim of this work was therefore to study vancomycin stability in syringes and assess its use (pH, osmolality, number of particles) during a continuous 24-hour infusion with and without inline filters” Masse et al (2020).
Closed-system drug transfer device reduces contamination during bolus injection – Full Text

“Use of a CSTD significantly decreased the number of spills and level of contamination compared with the currently used technique and, consequently, the use of such devices offers a safer working environment for nurses” Marler-Hausen et al (2020).
Central catheter surface type encourages biofilm formation
“This information provides guidance in regard to the preparation of hyperosmolar total parenteral nutrition and the engineering of CVC surfaces that can minimize the risk of catheter-related bloodstream infections caused by S. capitis in the NICU” Qu et al (2020).
Medication errors and needlestick injury exposure to student nurses
“Nursing students are subject to clinical safety-related events during their practices, mostly concerning medication errors and sharps and needlestick injuries” García-Gámez et al (2020).
Chlorhexidine allergy associated with IV site skin cleansing

“We present a case-report of a teenager, treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia who developed an anaphylactic shock after repeated chlorhexidine use for skin disinfection at the insertion of a central venous catheter during his chemotherapy treatment” Devinck et al (2020).
Management of ampicillin infusions in the outpatient setting
“The use of ampicillin in the outpatient setting has traditionally been avoided due to its short half-life and instability in solution. However, recent in vitro data and two recent case series have supported the safe and effective administration of ampicillin by continuous infusion in the community” Parsonson et al (2020).
How to implement an emergency department vascular access team
“It is possible that hospitals benefit from the services of vascular access specialists to provide higher quality care” Bell and Spencer (2020).
Study-related needlestick injuries among academic students – Full Text
“Needlestick and sharps injuries (NSIs) as well as lab accidents play a pivotal role. Furthermore, above 40% of the study-related commuting accidents were cycling accidents”
Peripherally inserted central catheter tip damages tricuspid valve

“For echocardiographers, precise evaluation of the position of the PICC tip and the detection of endocarditis is important to devise the optimal clinical strategy” Chen et al (2020).
Vancomycin nephrotoxicity when administered as a continuous 24 hour infusion
“We retrospectively investigated the rate of nephrotoxicity and associated risk factors in outpatients on VCI between May 2013 and November 2018” Chambers et al (2020).
UEDVT in children with heart failure on continuous IV milrinone

“The aim of this study was to determine the incidence of thrombosis, identify thrombosis risk factors, and determine the impact of anticoagulation in pediatric patients receiving continuous milrinone via CVC” Vesper et al (2020).
Blood culture collection kit with checklist amongst methods to reduce false positives – Full Text

“Apart from teaching and training, the concept of blood culture collection kit with checklist and dedicated blood collection team was found to be vital in reducing blood culture contamination” Shaheen et al (2020).
Central catheter-associated complications in the PICU
“We aimed to identify the occurrence and risk factors for unplanned catheter removal due to catheter-associated complications and the effects on catheter survival probability in a PICU” Shimizu et al (2020).
IV site observation during total intravenous anaesthesia – Full Text
“These publications also recommend processed EEG ‘depth of anaesthesia’ monitoring when TIVA is used with a neuromuscular blocking (NMB) drug and the TIVA guidelines recommend a lower threshold for its use when the i.v. access site is not continuously visible” Davies et al (2020).
Ultrasound visualization of central venous catheter guidewire

“A chest radiograph can be waived provided the ultrasound examination (identification of the guidewire and exclusion of puncture-related complications such as pneumothorax) is unambiguous” Zick et al (2020).
Antimicrobial susceptibility of central line-associated bloodstream infections
“The CLABSI rates at a well-equipped tertiary care hospital are still significantly higher than the USA benchmarks. Alarming rates of drug resistance in Gram-negative pathogens were seen” Singhal et al (2019).
When should intraosseous access be considered a first-line option?
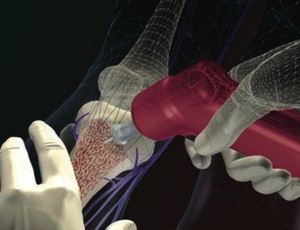
“In cases in which there is an urgent need for medications and fluid resuscitation, whether in infants, children, or adults, and immediate intravenous access is not easily obtainable, intraosseous access should be considered as a first-line option” DeBoer et al (2020).
Practical anatomical landmark for central venous catheter tip positioning
“This study aimed to evaluate a new, simple, and feasible method based on surface anatomy for the proper placement of tunneled CVC in the left internal jugular vein for hemodialysis or chemotherapy” Salimi et al (2020).
Protocols for massive transfusion in pediatric trauma
“Implementation of PMT protocols have been limited in showing significant improvement of overall pediatric trauma mortality but may reduce associated morbidity” Kinslow et al (2020).
Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular cannulation may reduce CLABSI in preterm infants – Full Text
“The objective of this study was to assess the risk of central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI) of ultrasound (US)-guided cannulation of the brachiocephalic vein (BCV) compared to standard epicutaneous cava catheters (ECCs) in preterm infants” Oulego-Erroz et al (2020)
Preventing infusion-related pain during Oxaliplatin infusion

“In this retrospective cohort study we compared the incidence of infusion-related pain in patients treated with oxaliplatin with or without simultaneous fluid infusion” van Ravensteijn et al (2020).
Using purchase data to determine the incidence of sharps injuries
“This study demonstrated the use of purchase data to determine the incidence of sharps injuries in a major tertiary referral hospital in Australia” Wong et al (2020).
What is the impact of CLABSI in adult home parenteral nutrition patients

“We investigated potential predictors of CLABSI to determine a predictive model in a cohort of adult HPN patients” Xue et al (2020).
Iatrogenic humeral neck fracture after intraosseous vascular access
“It is important for radiologists to recognize the findings related to intraosseous access as well as this complication with its characteristic locations and morphology” Hopp et al (2020).
Pediatric intracavitary ECG-guided positioning of central vascular access device
“This study evaluated whether unnecessary ionizing radiation exposure could be spared in the pediatric population when intracavitary electrocardiography is used to guide catheter placement” Raffaele et al (2020).

